Understanding the Different Types of Oral Magnesium and Their Bioavailability
Magnesium is a critical mineral involved in over 300 biochemical reactions in the body, supporting muscle function, nerve health, bone strength, and cardiovascular health. However, not all magnesium supplements are created equal. Understanding the different types of oral magnesium and their bioavailability can help you choose the best option for your specific needs. This guide explores the various forms of magnesium, their absorption rates, and key factors to consider when purchasing a magnesium supplement.
What is Magnesium and Why is it Essential?
Magnesium is an essential mineral that plays a vital role in numerous bodily functions, including energy production, DNA synthesis, and muscle contraction. It helps regulate blood pressure, supports bone health, and even influences mood and cognitive function. Despite its importance, many people do not get enough magnesium from their diets, leading to symptoms like muscle cramps, fatigue, and irritability.
Types of Oral Magnesium Supplements
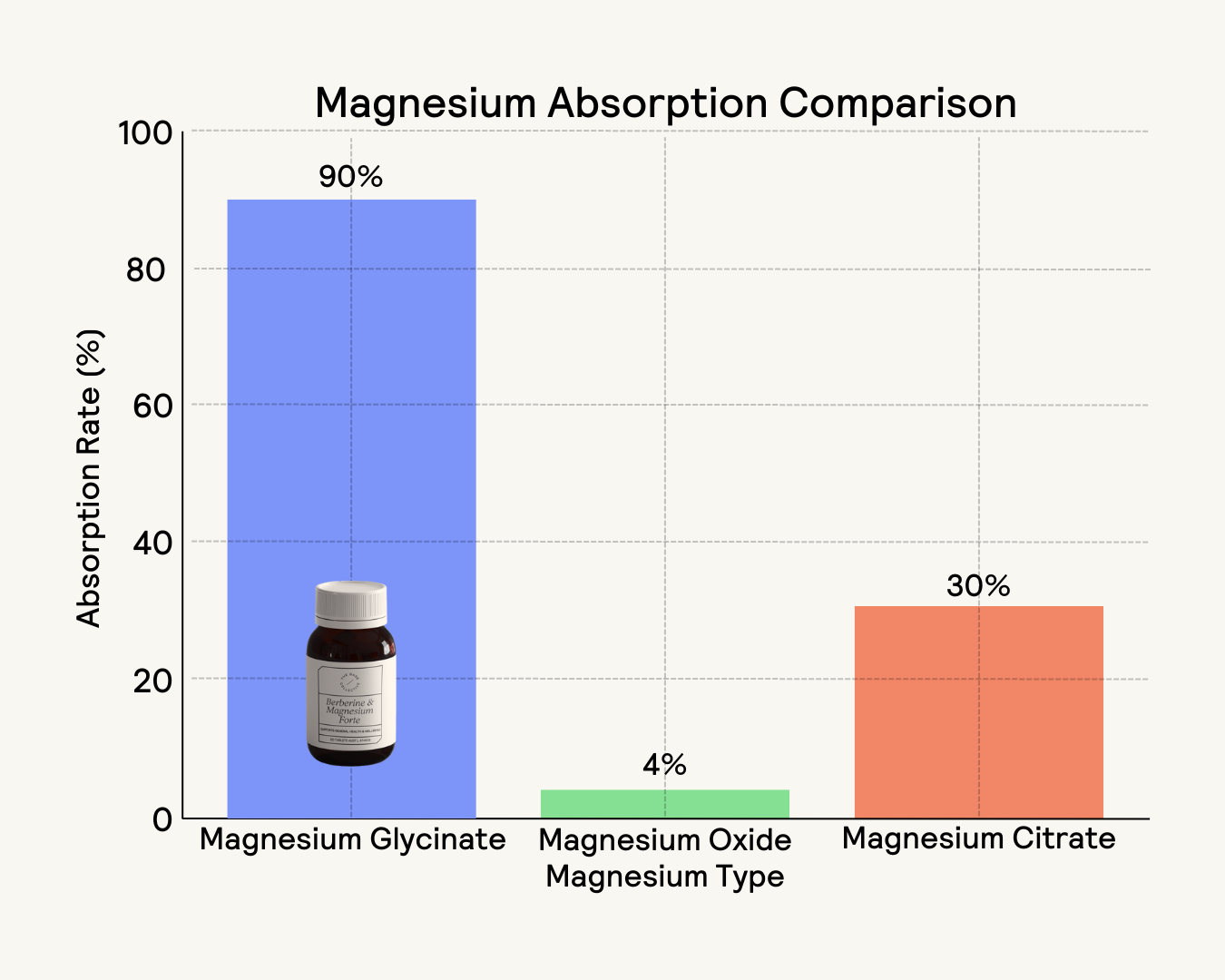
Magnesium Oxide
Magnesium oxide is one of the most common forms of magnesium supplements. It contains a high percentage of elemental magnesium but has a relatively low absorption rate, often around 4%. This form is typically used for relieving constipation and addressing magnesium deficiencies but may not be the best choice for those seeking to increase overall magnesium levels due to its poor bioavailability.
Magnesium Citrate
Magnesium citrate is more bioavailable than magnesium oxide, making it a popular choice for addressing magnesium deficiency and supporting digestive health. It is often used as a mild laxative and can be easier on the stomach. However, it still provides a moderate amount of elemental magnesium.
Magnesium Glycinate
Magnesium glycinate is a highly bioavailable form of magnesium that is gentle on the stomach and less likely to cause digestive upset. It is bound to the amino acid glycine, which may have calming properties, making it an excellent choice for those looking to improve sleep quality, reduce anxiety, and support muscle recovery.
Understanding Magnesium Bioavailability
Bioavailability refers to how much of a nutrient your body can absorb and use. Magnesium’s bioavailability depends on the form it is in, as well as factors like digestive health and the presence of other nutrients. Choosing a form with high bioavailability ensures you get the most benefit from your supplement.
Elemental Magnesium: The Critical Metric
When choosing a magnesium supplement, it’s crucial to consider the amount of elemental magnesium it contains. Elemental magnesium is the actual amount of magnesium available for absorption. For example, magnesium oxide has a high elemental content but low bioavailability, while magnesium glycinate offers a more moderate amount of elemental magnesium but is much more easily absorbed.
What to Look for When Purchasing an Oral Magnesium Supplement
-
Choose a form with high bioavailability, like magnesium glycinate or citrate, if you want better absorption.
-
Check the elemental magnesium content to ensure you are getting an effective dose.
-
Avoid products with unnecessary fillers or artificial additives that may reduce absorption or cause digestive issues.
-
Consider your specific health goals, such as improved sleep, muscle recovery, or heart support, when selecting a magnesium type.
Final Thoughts and Recommendations
Choosing the right magnesium supplement can significantly impact your overall health. By understanding the differences in absorption and elemental content, you can make a more informed choice that aligns with your wellness goals. For those looking for a high-quality magnesium supplement, consider our Berberine and Magnesium Glycinate supplement for optimal absorption and synergistic health benefits.
The information provided by The Base Collective is not intended to be used as medical advice and should not take the place of professional or medical advice. Always seek the guidance of your doctor or other qualified health professionals with any questions you may have regarding your health or medical condition.







Leave a comment
This site is protected by hCaptcha and the hCaptcha Privacy Policy and Terms of Service apply.